Spatial data infrastructure
According to the Estonian Spatial Data Act, the management and development of the Estonian geoportal is the responsibility of the Land and Spatial Development Board. The Land and Spatial Development Board collects all obligatory data about the appropriate public authorities, makes them available in the geoportal and forwards them to the European Commission INSPIRE Geoportal.
Legislation
INSPIRE Coordination in Estonia
The Ministry of the Environment is the responsible body for the implementation of the INSPIRE directive in Estonia. In accordance with the Spatial Data Act, passed on 28 February 2011, the contact point was also appointed to be the Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board.
The national implementation of the INSPIRE Directive is coordinated by Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board with maintaining national SDI portals like Estonian Geoportal and Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board geoportal. Also providing support and guidance for national data owners.
Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board is responsible for data harmonizing and providing Estonian catalog service and most of the INSPIRE valid spatial data services with collaboration Information Technology Centre of the Ministry of the Environment.
As INSPIRE coordinator Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board has representatives in MIG-T and MIG.
Estonian INSPIRE Coordination Structure
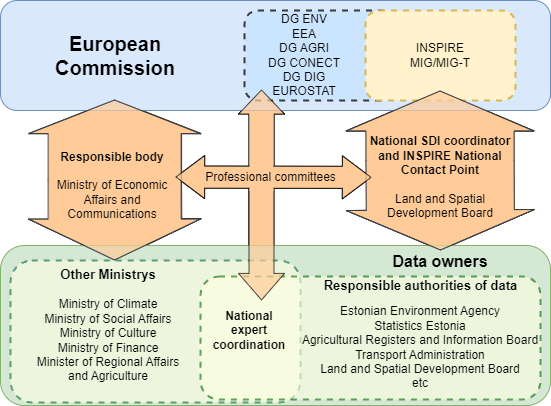
In most cases, the Ministries are the data owners by law, but their subdivisions are responsible authorities for the data. Ministries have representatives in different committees of European Commission to support understanding political and technical needs of other committees for INSPIRE data. Ministries subdivisions work on a daily basis with Estonian Land and Spatial Development Board technical personnel to support data harmonization to INSPIRE valid data.
Spatial Data Infrastructure
Spatial data infrastructure (SDI) ensures that geographically references data held by public authorities, i.e. national spatial data, are available and reliable.
In order to achieve availability and reliability, we need data, technologies, legal regulation and mutual agreements. Thus, SDI is much more than simply a database or geographic information system.
Spatial data
Spatial data is data that identifies the geographic location of features and boundaries on Earth. Such features are e.g. buildings, roads, fields, forests, protected areas, cadastral parcels, lighthouses, etc. As a rule, these data are depicted on map, i.e. they are used for map production.
There are many national databases in Estonia that contain spatial data: Estonian topographic database, cadastral register, register of construction works, register of roads, environmental register, address data system, etc. It is extremely important that these spatial data are of high quality, well described and easily discovered.
Technologies
In order to be able to search, discover and use spatial data from different databases, we need technologies that enable us to do so. SDI technology consists of hardware, i.e. powerful servers and other appropriate equipment, and software to create services through which spatial data are made available.
Regulation and agreements
The objective of SDI will be achieved when the interoperability of different spatial data generates a considerable added value. It means that the provided data and services must conform to certain standards. Spatial data must be unambiguous, i.e. semantically described; they must contain metadata with a common structure.
All the above is regulated in the world and also in Estonia with different regulations starting from laws and ending with recommendations, cooperation agreements and guidelines. In Estonia, this field is regulated by the Spatial Data Act and Public Information Act, Implementing Rules of the INSPIRE Directive and different regulations, development plans and framework documents.